“I think any kind of exploration should always try to acquire the highest level of imaging. That’s how you engage people — you can put them there, give them the sense they’re standing there on the surface of Mars.”
.
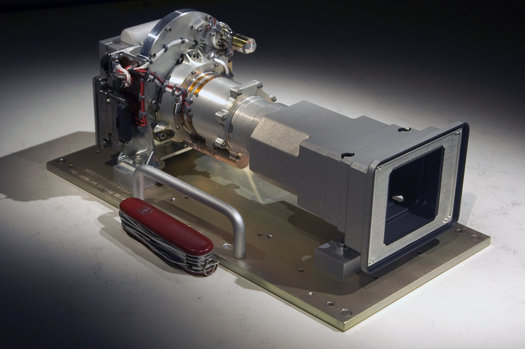
For obvious reasons the pro-active visionary heroics of Oscar-winning director James Cameron have become a running theme on this blog. The director of “Avatar” and many other sci-fi flicks, “Titanic,” and technologically demanding undersea documentaries, is now helping NASA develop a high-resolution 3D camera for the next Mars rover, SUV-sized Curiosity, due to launch in 2011.
.
Remember the beautiful Mars imagery NASA’s Mars rover, Spirit, captured during its journey to the Red Planet? Now imagine high-definition color 3D video from the surface of Mars at eye-level, in motion, at walking pace: sunrises and sunsets, stars after midnight, vistas stretching for miles.
.
Zoom lenses will allow for “cinematic video sequences in 3-D on the surface.”
.
“The fixed focal length [cameras] we just delivered will do almost all of the science we originally proposed. But they cannot provide a wide field of view with comparable eye stereo. With the zoom [cameras], we’ll be able to take cinematic video sequences in 3D on the surface of Mars. This will give our public engagement co-investigator, James Cameron, tools similar to those he used on his recent 3D motion picture projects,” said Michael Malin of
Malin Space Science Systems, Inc, the company which developed the Mastcams.

.
“[NASA Administrator Bolden] actually was really open to the idea. Our first meeting went very well. It’s a very ambitious mission. It’s a very exciting mission. (The scientists are) going to answer a lot of really important questions about the previous and potential future habitability of Mars.”
.
“We so desperately need not to blow it,” Cameron said of the first opportunity in decades to consider moving human exploration beyond low Earth orbit. Cameron has lamented that space exploration stalled — because of political compromises — after the Apollo moon landings. Rather than being a jumping off point to future great adventures, the space shuttle and International Space Station ultimately “formed a closed-loop ecosystem for self-justification.”
.
Now, the agency has a chance to move beyond that and chase mankind’s “greatest adventure” — landing humans on Mars.
.
“Where does the money come from? From working people, with mortgages and kids who need braces. Why do they give the money? Because they share the dream.” They need reasons to stay engaged: from telling them the ways space exploration has provided them with tools that improve their daily lives to helping them to be more interactively involved in the missions.
.
NASA’s focus has been on hardware instead of people, partly because the agency shields its people from the public. Instead, in an era when American kids and adults need inspiration, NASA needs to do a better job of selling its astronauts and scientists as heroic people.
.
“Our children live in a world without heroes,” he said. “Your kids need something to dream about. We need this challenge to bring us together.” I think that any kind of exploration should always try to acquire the highest level of imaging. That’s how you engage people — you can put them there, give them the sense that they’re standing there on the surface of Mars.”
.
“The [1997] Sojourner Rover became a character to millions of people, a protagonist in a story. How long is it going to survive, could it perform its mission? It wasn’t anthropomorphic in any way, there was absolutely no emotion in a little solar powered machine that was being commanded from eighty million miles away, and yet people thought of it as a character. The reason we thought of it as a character is that it represented us in a way. It was our consciousness moving that vehicle around on the surface of Mars. It’s our collective consciousness — focused down to that little machine – that put it there. So it was a celebration of who and what we are. It takes our entire collective consciousness and projects it there – to that point in time and space. That’s what the Sojourner Rover did.”
.
“I was involved in a private company that was going to try to land two rovers on the Moon. That collapsed in the dot com crash – they ran out of money. I’m loosely involved with people who are going to be doing future robotic missions to Mars. I’m involved in terms of imaging, and of how imaging might be improved in terms of story telling. I’ve been very interested in the Humans to Mars movement –the ‘Mars Underground’ — and I’ve donea tremendous amount of personal research for a novel, a miniseries, and a 3-D film.”
.
Mars is real, non-threatening, a living character with which humanity must become familiar and comfortable. Stay tuned for a forthcoming post explicitly about Cameron’s Mars film work, yet again.









































 . “That party’s been join’ on down there for a billion years – and its going to be going on for the next billion years. They’re just doing their thing – it’s got nothing to do with us, the sun could go out tomorrow – and they wouldn’t know and they wouldn’t care.”
. “That party’s been join’ on down there for a billion years – and its going to be going on for the next billion years. They’re just doing their thing – it’s got nothing to do with us, the sun could go out tomorrow – and they wouldn’t know and they wouldn’t care.”